Free Body Diagram Tension In A Rope
How to draw free body diagram. Tension T acts upward on the lamp while the force of gravity pulls down with force w the weight of the lamp.
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn And9gcsrunddnqgc879r8o4xwtddqfh5glacfj5zsnovz27k1 Jp7raw Usqp Cau
Because the stationary box is on a surface there is a.

Free body diagram tension in a rope. Free-body diagram of Team2. T 80 55 745 N. B free body diagram of point P.
F net mass acceleration F net 4070005 55 N. The formula for tension becomes complex when we attach more than one weight. In an ideal system the massless and frictionless pulleys do not dissipate energy and allow for a change of direction of a rope that does not stretch or wear.
The rod has a mass of 14 kg and there is an angle of 34 between the rope and the rod. Two blocks are connected by a light string passing over a pulley of radius 015 m and moment of inertia I. One is the tension in the bottom portion of rope pulling down and he also has the force of.
Therefore a rope under tension pulls in both directions. In an ideal system the massless and frictionless pulleys do not dissipate energy and allow for a change of direction of a rope that does not stretch or wear. The force that the rope exerts on the upper block is -T or T pointing downward.
Another example showing how to use free body diagrams and Newtons 2nd law to solve a physics problem. Ropes can be used to pull heavy objects. Every point in the rope at which it transitions from contact with the pulley to noncontact or at which it transitions from noncontact to contact with the pulley counts as a separate contact point between the object and the rope for the purposes of constructing a free body diagram of the situation.
The free-body diagram is shown below with the support force. B What are the two components of the support force exerted by the hinge. A What is the tension in the rope.
The forces acting on team1 are tension and the pulling force of 80 N. The lamp is not accelerating so the force up must equal the force down. Applying same logic for team2.
This physics video tutorial explains how to calculate the normal force on a horizontal surface when a downward force is applied or when an upward tension for. A system with two blocks an inclined plane and a pulley A free body diagram for block m 1 left of figure below 1 The weight W 1 exerted by the earth on the box. Identify the forces acting on the box.
A rope cannot push an object. 1 We sketch what is happening. Solving for T gives TF_0-5ga.
Three forces upper part of figure below 1 Tension T 1 2 Tension T 2 3 Tension T 3 Example 8. So then value of tension in the rope is 745 N. Free body diagrams The mechanical advantage of a pulley system can be analysed using free body diagrams which balance the tension force in the rope with the force of gravity on the load.
Free Body Diagram Introduction. The force balance on the upper block is F_0-T-5g5a where T is the tension in the rope at the top of the rope. Lets draw the free-body diagram of the sphere.
Sketch of the sphere hanging from the two ropes attached to the ceiling. Setting up the Free-Body Diagram Step 1. The mechanical advantage of a pulley system can be analyzed using free body diagrams which balance the tension force in the rope with the force of gravity on the load.
The box has mass so it also has weight a force acting downward. Attached to the box there is a rope with tension applied. The first rope makes an angle of 30 with the ceiling while the second rope makes an angle of 45 with the ceiling.
Because the box is on a surface there is a normal force acting perpendicular to the surface. The net force is the vector sum of these two forces. Identify the forces present.
Endgroup Chet Miller Aug 26 16 at 023. 30 45. October 9 2020.
Therefore a rope under tension pulls in both directions. B Determine FTA and FTB the tensions in the two parts of the string. F net 80 T.
Draw the object with no extra features. In terms of magnitudes this means. Draw the object with no extraneous features Step 2.
The blocks move toward the right with an acceleration of 100 ms2 along their frictionless inclines See figure below. What is the tension in the chain. A free body diagram is a picture of the forces which act on an object and is the first and perhaps the most important step in solving force problems.
As always begin with a free body diagram. In this problem a pot is hanging from the ceiling by. Let us calculate net force for team2 first.
A Draw free-body diagrams for each of the two blocks and the pulley. The box has mass so it should also have weight and a force acting downward. And the free body diagram diagram for our superhero has a single force going upwards which is this tension in the top portion of rope and two forces down.
A free body diagram is a picture of the forces which act on an object and is the first and perhaps the most important step in solving force problems. Whenever we pull a rope tension is developed in the rope. The formula for tension is simple when we consider one weight attached to the rope it is equal to the force applied.
Free Body Diagram Tension
The net force is always equal to the mass times the acceleration. Solutions to the assigned problems.

An Easy Guide To Understand Free Body Diagrams In Physics Science Struck
B В с 4 ft G 4125 ft 25 ft S A 15 ft 3 ft.

Free body diagram tension. Include an outline of your solution proceedure. A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. - The magnitude of the tension on the cart is the same as the magnitude of the tension on the hanging mass - The normal force on the cart is normal to the track.
The net force on team1 is the sum of the forces. F1 is negative because it is opposite to the direction of the net force. How to draw free body diagram.
That is latex F_textnetne 0 latex. We may call it the apparent weight of the fish. A couple of important things to note.
The box has mass so it should also have weight and a force acting downward. Commonly air resistance and friction are neglected. Also we use two free-body diagrams because we are usually finding tension T which may require us to use a system of two equations in this type of problem.
Once we have drawn an accurate free-body diagram we can apply Newtons first law if the body is in equilibrium balanced forces. F net T - mg. Please explain whether Compression or Tension is acting on them respectively by using Free body diagram and proper explanation.
Free body diagram of Team 1 The forces acting on Team1 are F1 pull by the team and T. The forces acting on the fish are shown in the free-body diagram. Remember that a free-body diagram must only include the external forces acting on the body of interest.
A free-body diagram is a diagram that is modified as the problem is solved. Upload an image of your free body diagrams below. Assume a frictionless ground.
How do I know which one to use. Dynamics Chapter Problems - 8 v 20 2009 by Goodman Zavorotniy c. This is the value the scale reads.
A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. The external environment other objects the floor on which the object sits etc as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects are omitted in a free-body diagram. Because the stationary box is on a surface there is a.
It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. T is the tension supplied by the scale. Tension is positive because it acts in direction of the net force.
Draw all free body diagrams needed to find the tension in cable FE. This is the tension force. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
Why is it T-mg sometimes and mg-t other times. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. Sal defines and compares tension weight friction and normal forces using free body diagrams.
Draw a free-body diagram for each block showing all applied forces to scale. Finding this force requires a system of equations. Solving the Free-Body Diagram In order to solve the problem the force on the rope necessary to move the box up the incline must be found.
Following that we know that P is under tension and R is under compression. Draw a free body diagram fbd using the skills and definitions above. Normally a free body diagram consists of the following components.
I was doing gravitation questions where T-mgFc. The net force on the fish is. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be drawn.
The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. Two boxes are placed on a horizontal frictionless surface as shown above. Draw the object with no extra features.
The number of forces acting on a body depends on the specific problem and the assumptions made. Here is the free body diagram with the forces on both objects. Identify the forces acting on the box.
Find the tension force in the string between two objects. Box A has a mass of 10 kg and box B has a mass of 16 kg. F net T - w.
Identify when the forces above are acting on a body AND describe their direction of influence. Free body diagrams with tension Thread starter username Start date Jul 21 2007. Human muscle system the muscles of the human body that work the skeletal system that are under voluntary control and that are concerned with the following sections provide a basic framework for the understanding of gross human muscular anatomy.
That is latex F_textnet0 latex or Newtons second law if the body is accelerating unbalanced force. Identifying the forces we. Although there is currently one known variable the weight there are three unknown variables.
Can I resolve W in this way so that we have a force in the direction of P and parellel to R. Jul 21 2007 1 username 7 0. A force of 54 N is pushing box A.
My question is for free body diagrams with tension on top and mass hanging from the bottom.
Free Body Diagram Physics Examples
A book on a table In this example there are two forces acting on a book at rest on a table. A free body diagram models the forces acting on an object.

Newton S 2nd Law 15 Of 21 Free Body Diagrams One Dimensional Motion Youtube
In a hypothetical situation without external forces friction and air resistance only the three remaining forces will act on the vehicle.
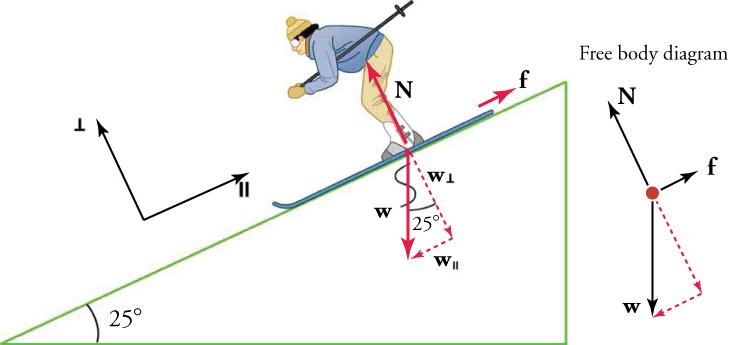
Free body diagram physics examples. A free body diagram sometimes called a force diagram is a pictorial device often a rough working sketch used by engineers and physicists to analyze the forces and moments acting on a body. There will be cases in which the number of forces depicted by a free-body diagram. The Free Body Diagrams Interactive is a skill-building tool that allows the learner to interactively construct free-body diagrams for 12 physical situations.
Construct free-body diagrams for different situations. Okay so first of all we know that Bobs gonna pull on the cart Force F B and the cards also gonna have forced down due to gravity and a force up due to the ground pushing on it. Published 2008-10-15 Author.
The first step in describing and analyzing most phenomena in physics involves the careful drawing of a free-body diagram. That is F n e t 0 or Newtons second law if the body. Welcome to our second example video on free body diagrams.
Draw the forces acting on the bottle. An example of a free-body diagram is shown at the right. Each situation is described and the learner clickstaps on-screen buttons to select forces that.
At the same instant the second player kicks with force 215 N at 15 east of south. This video lesson explains how to analyze a physical situation and construct a free-body diagram that shows the types of forces the direction of the forces. If the tension in the rope is 160 N and the coefficient of friction between the crate and the floor is 55 what is the net force on the crate and the net work done on the crate.
This video will continue. A free body diagram sometimes called a force diagram is a pictorial device often a rough working sketch used by engineers and physicists to analyze the forces and moments acting on a body. Examples of Free Body Diagrams with Detailed Explanations Example 1.
Free Body Diagrams Practice Problems Construct free-body diagrams for the various situations described below. The object or body is usually shown as a box or a dot. So in this problem were going to go back to a similar problem that we considered in the initial video where were looking at two boxes that are touching each other and were going.
Diagram the forces acting on the girl. First of all it will help if we draw a free body diagram for each of these. The first step in describing and analyzing most phenomena in physics involves the careful drawing of a free-body diagram.
The free body diagram of a car traveling at a constant speed consists mainly of five forces when considered in an actual situation. Two soccer players simultaneously kick a stationary soccer ball on the flat field. A bottle is resting on a tabletop.
A girl is suspended motionless from a bar which hangs from the ceiling by two ropes. The first player kicks with force 162 N at 90 north of west. Find the acceleration of the ball in ˆi and ˆj form.
A book is at rest on a table top. The soccer ball has mass 0420 kg. Diagram the forces acting on the book.
In this section we have listed free diagrams considered under different scenarios. An example of a resting object with weight and normal forces balanced is your book sitting on a table. Unbalanced force gets involved.
Remember that a free-body diagram must only include the external forces acting on the body of interest. Free-Body Diagram Example Problem 1 A wooden crate with a mass of 800 kg is pulled 25 m across a concrete floor by a man holing a rope 32 above the horizontal. Free-body diagrams have been used in examples throughout this chapter.
Free Body Diagram Examples. We have a free body diagram for the cart and we have a free body diagram for our generic beast of burden or Bob. An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree.
An egg is free-falling from a nest in a tree neglecting the air resistance what would the free body diagram look like. Free-body diagrams have been used in examples throughout this chapter. The body itself may consist of multiple components an automobile for example or just a part of a component a short section of a beam for example anything in fact that may be considered to act as a.
Thank-you for contributing it. Pictures like this are a huge help to those of us who are learning. An example of an object with the force of gravity and the normal force balanced that is moving at a pretty constant velocity is a hockey puck gliding across the ice.
1 The weight W exerted by the earth on the book 2 The normal force N exerted by the table on the book. Once we have drawn an accurate free-body diagram we can apply Newtons first law if the body is in equilibrium balanced forces. The forces are shown as thin arrows pointing away from the centre of the box or.
Remember that a free-body diagram must only include the external forces acting on the body of interest. Thio consider the problem of drawing free body diagrams for multiple objects. This was a great help to me in Physics recently.
T he free-body diagram above depicts four forces acting upon the object. Objects do not necessarily always have four forces acting upon them. Other Types of Forces Force of Friction.
I was able to modify the bare bones of this to illustrate the forces on a ramp for my high school students. These vectors are that of friction gravity normal force air resistance and engine driving force. The body itself may consist of multiple components an automobile for example or just a part of a component a short section of a beam for example anything in fact that may be considered to act as a.
