Free Radicals Definition Biology
Free radicals are chemical species possessing an unpaired electron that can be considered as fragments of molecules and which are generally very reactive. An atom or atom group carrying an unpaired electron and no charge.
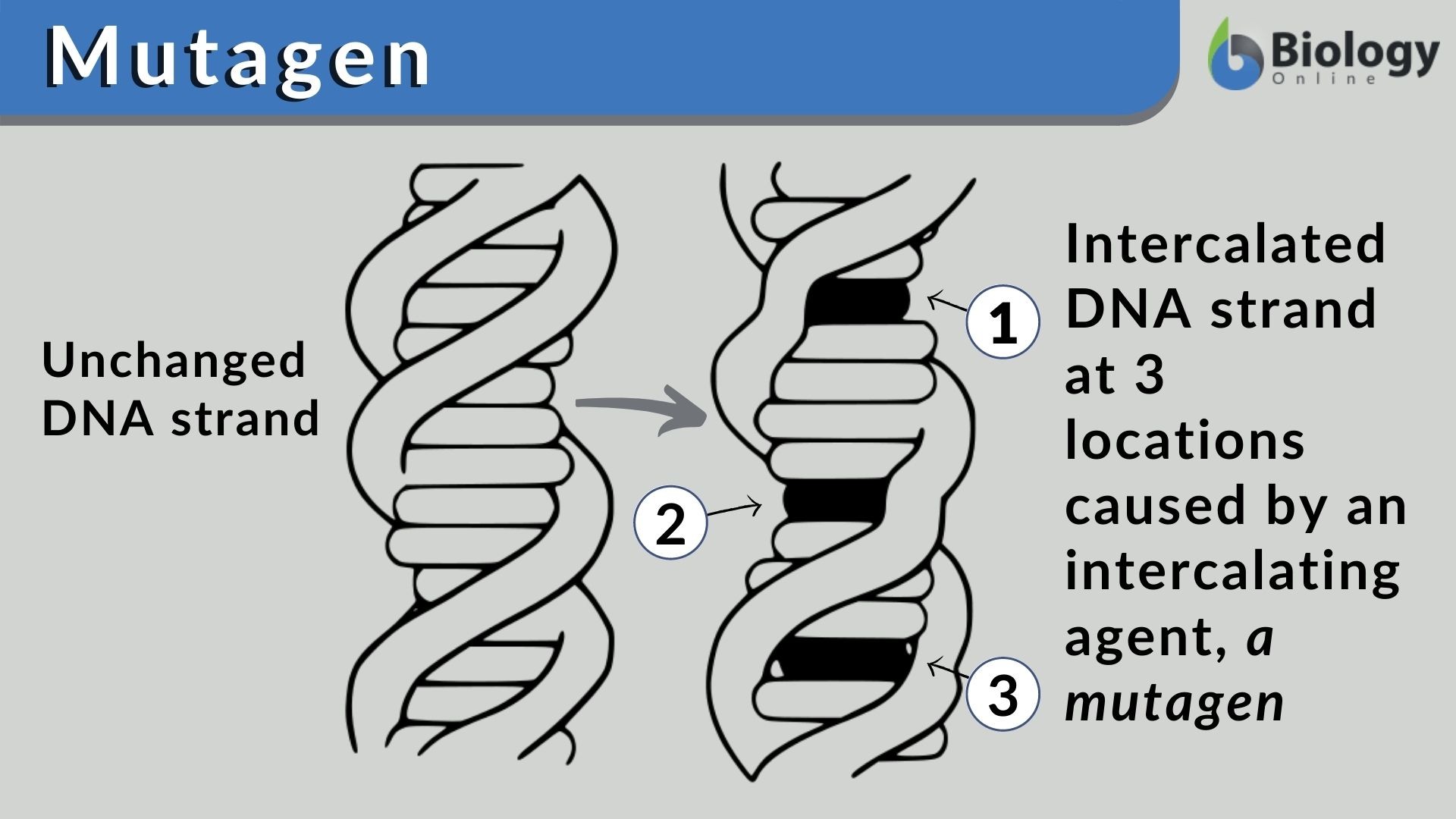
Mutagen Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
This is just my understanding of it in the m.

Free radicals definition biology. They are produced continuously in cells either as accidental by-products of metabolism or deliberately during for example phagocytosis. Free radicals are linked to aging and a host of diseases. Over time this damage accumulates and causes us to experience aging.
Free radicals are unstable atoms that can damage cells causing illness and aging. An unusual family of enzymes the superoxide dismutases protect against the deleterious actions of this. The most common definition of free radicals is molecules or molecular fragments containing one or more unpaired electrons in atomic or molecular orbitals 3.
American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language Fifth Edition. The free radical theory of aging asserts that many of the changes that occur as our bodies age are caused by free radicals. Free radicals are capable of reversibly or irreversibly damaging compounds of all biochemical classes including nucleic acids protein and free amino acids lipids and lipoproteins carbohydrates and connective tissue macromolecules.
Eg hydroxyl and methyl Free radicals may be involved as short-lived highly active intermediates in various reactions in living tissue notably in photosynthesis. Human beings contain 1000020000 free radicals which attack each and individual cell of our body. Instead a radical specifically a free radical is the term used to describe a particle that has an unpaired electron.
Definition of free radical. Damage to DNA protein cross-linking and other changes have been attributed to free radicals. Definition and Structure of Free Radicals.
In animal tissues free radicals can damage cells and are believed to accelerate the progression of cancer cardiovascular disease and age-related diseases. There is some evidence to support this claim. An electron is the negative portion of an atom and is found outside the.
An especially reactive atom or group of atoms that has one or more unpaired electrons especially. Free Radicals In chemistry a radical more precisely a free radical is an atom molecule or ion that has unpaired valence electrons or an open electron shell and therefore may be seen as having one or more dangling covalent bonds. A radical in its usually transient uncombined state.
Due to this lack of a stable number of outer shell electrons they are in a constant search to bind with another electron to stabilize themselvesa process that can cause damage to DNA and other parts of human cells. Free radicals are atoms that contain an unpaired electron. A type of unstable molecule that is made during normal cell metabolism chemical changes that take place in a cell.
I created this video as I struggled to get my head around this when I was first learning about oxidative stress. The reactive superoxide radical O2- formerly of concern only to radiation chemists and radiobiologists is now understood to be a normal product of the biological reduction of molecular oxygen. An atom or group of atoms that has at least one unpaired electron and is therefore unstable and highly reactive.
One that is produced in the body by natural biological processes or introduced from an outside source such as tobacco smoke toxins or pollutants and that can damage cells proteins and DNA by altering their chemical structure. Free radicals can build up in cells and cause damage to other. Free radicals are uncharged very reactive and short-lived molecules.
This damage may play a role in the development of cancer and other.
